





|
|
| |
The mycotoxin fusarin C has been isolated from
F. graminearum, Fusarium moniliforme (= F. verticillioides,
teleomorph Gibberella fujikuroi = G. moniliformis) and
Fusarium venenatum. Structural characterization of the compound and
isotope labelling experiments (13C acetate) suggested a mixed biosynthetic
origin by including both polyketide and amino acid motifs (Gelderblom et
al., 1984). The presence of methyl groups directly on the polyketide chain
suggested that the involved PKS would pose a carbon methyltransferase domain
(CMeT). The fusarin C PKS (fusA or FUSS) was isolated by probing a cDNA
library with a probe made with degenerated primers targeted against the CMeT
domain using F. moniliforme cDNA as temple. Sequence analysis of the
deduced PKS amino acid sequence (3951 aa) revealed that the PKS in fact was
a hybrid of a PKS and a non-ribosomal peptide synthase (PKS-NRPS) with the
following domain architecture: KS-AT-DH-CMeT-ER?-KR-ACP-C-A-T-R. Where the
PKS domains (KS-AT-DH-CMeT-ER?-KR-ACP) are responsible for synthesis of the
linear heptaketide chain, while the NRPS domains (C-A-T-R) adds a homoserin
to the PKS chain. Targeted replacement of fusA confirmed that it was
required for the biosynthesis of fusarin C and also allowed for the
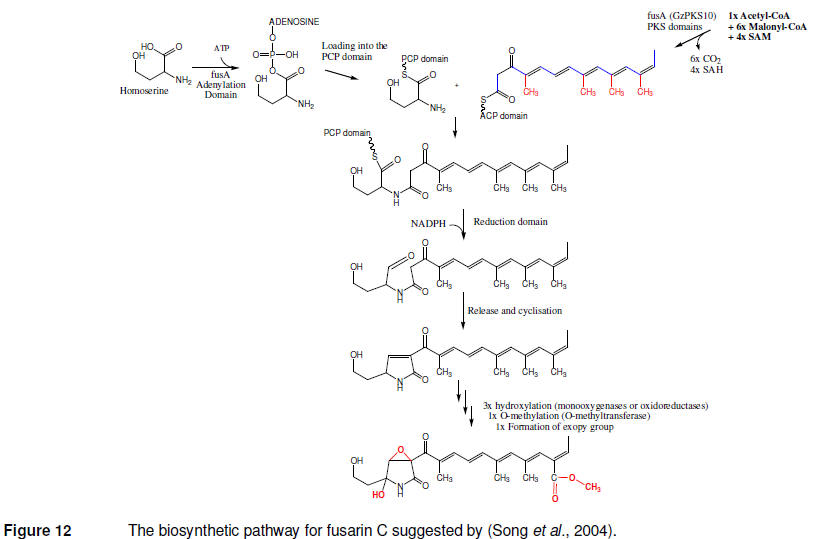
formulation of a model for the biosynthesis of the compound (Figure 12).
|
| |
Later an analysis of the F. graminearum
PH-1 genome has re-identified the fusA PKS-NRPS, renamed FgPKS10 (FG12100)
in (Gaffoor et al., 2005), and targeted replacement confirmed the results
(Song et al., 2004). The genes encoding the proposed modifying enzymes have
not been identified; however the genes surrounding the fusA gene in F.
graminearum includes both cytochrome P450-dependent monooxygenases, a
FAD/FMN-dependent dehydrogenase, a S-adenosyl methionine-dependent O-methyl
transferase and an acyl hydrolase suggesting the existence of a gene cluster
(Rees et al., 2007). |
References
 | Gelderblom,W.C.A., Marasas,W.F.O., Steyn,P.S., Thiel,P.G.,
Vandermerwe,K.J., Vanrooyen,P.H. et al. (1984) Structure Elucidation of
Fusarin-C, A Mutagen Produced by Fusarium-Moniliforme. Journal of
the Chemical Society-Chemical Communications: 122-124. |
 | Gaffoor,I., Brown,D.W., Plattner,R., Proctor,R.H., Qi,W.H., and
Trail,F. (2005) Functional analysis of the polyketide synthase genes in
the filamentous fungus Gibberella zeae (Anamorph Fusarium
graminearum). Eukaryotic Cell 4: 1926-1933. |
 | Song,Z.S., Cox,R.J., Lazarus,C.M., and Simpson,T.J. (2004) Fusarin C
biosynthesis in Fusarium moniliforme and Fusarium venenatum.
Chembiochem 5: 1196-1203. |
 |
Rees,D.O., Bushby,N., Cox,R.J., Harding,J.R., Simpson,T.J.,
and Willis,C.L. (2007) Synthesis of [1,2-C-13(2), N-15]-L-homoserine and
its incorporation by the PKS-NRPS system of Fusarium moniliforme
into the mycotoxin fusarin C. Chembiochem 8: 46-50. |
|

